NE HEALTH BUREAU
AHMEDABAD, APR 11
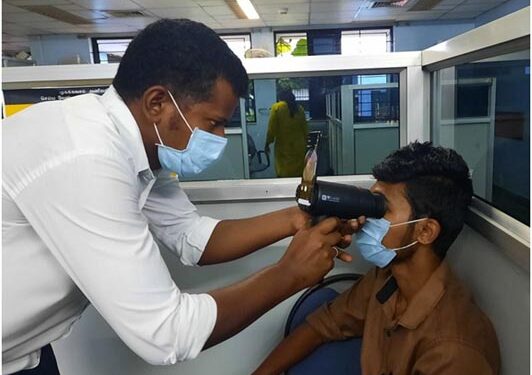
Samsung Electronics is repurposing older smartphones to enable greater access to ophthalmic health care in underserved communities around the world. Samsung partnered with the International Agency for the Prevention of Blindness (IAPB) and Yonsei University Health System (YUHS) in Korea to create medical devices that screen for eye disease by upcycling Galaxy smartphones that are no longer of use. This Galaxy Upcycling program is helping to address approximately 1 billion global cases of vision impairment that are preventable with proper diagnosis, says a release.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), at least 2.2 billion people have a form of vision impairment and almost half of these cases were preventable or have yet to be addressed. There is a large disparity in the prevalence of vision impairment depending on the affordability and availability of eye care services. This is estimated to be four times more common in low- and middle-income regions as compared to high-income regions, the release added.
“People around the globe face barriers to accessing fundamental health care, and we saw an opportunity to engineer smart, innovative solutions that reuse products to drive more sustainable practices and make a positive impact in our communities,” said Sung-Koo Kim, VP of Sustainability Management Office, Mobile Communications Business at Samsung Electronics.
“This program embodies Samsung’s belief that technology can enrich people’s lives and help us build a more equitable and sustainable future for all.”
In 2017, Samsung created the Galaxy Upcycling program to introduce innovative ways that Galaxy devices can make a positive impact. Through the program, an older Galaxy smartphone can become the brain of the Eyelike handheld fundus camera, which connects to a lens attachment for enhanced fundus diagnosis, while the smartphone is used to capture images. The Galaxy device then utilizes anartificial intelligence algorithm to analyze and diagnose the images for ophthalmic diseases and connects to an app that accurately captures patient data and suggests a treatment regimen at a fraction of the cost of commercial instruments. The unique and affordable diagnosis camera can screen patients for conditions that may lead to blindness, including diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and age-related macular degeneration.
“We were looking for an eye health diagnosis solution that was cost-effective to reach as many people as possible, and when we saw the performance of Samsung’s Galaxy smartphones, we wanted to integrate their upcycling efforts into our research,” said Dr. Sangchul Yoon of Yonsei University Health System.
“The combination of using multiple optical technologies and artificial intelligence, coupled with camera performance of a Galaxy smartphone, created an affordable medical device that was just as capable as a fundus camera used by medical professionals. This not only solved a health issue, but a growing environmental concern as well.”
Since 2018, Samsung has partnered with IAPB and Yonsei University Health System to benefit the lives and vision of more than 19,000 residents in Vietnam with its portable retinal camera. In 2019 alone, it supplied 90 portable ophthalmoscopes to health professionals operating in remote regions of the country without access to walk-in clinics. Now, Samsung has expanded the program to India, Morocco and Papua New Guinea. Samsung is also broadening its capabilities to new screening areas, including using upcycled Galaxy devices to create smartphone-based portable colposcopes to screen for cervical cancer and improve women’s accessibility to quality health care.